Patholgy Slides : Acute inflammation
اضغط على الصورة للتكبير - Click on image to enlarge size
Acute inflammation (exudative inflammation) is the immediate and early defensive response in the host, to all forms of injury. The main characteristic feature is the inflammatory infiltrate (exudate), which consists in: plasma liquid, plasma proteins, leukocytes, red blood cells and, sometimes, infective germs.
Depending on the etiology, localization and composition, exudative inflammation can be :
serous (first stage of lobar pneumonia, vesicles in herpetic infections or burns)
fibrinous (second stage of lobar pneumonia, fibrinous pericarditis, peritonitis or pleuresia, pseudomembranous colitis)
sero-fibrinous (the mixed form of previous two)
chataral (inflammation of mucus secreting mucosa from digestive or respiratory tract)
purulent or suppurative (localized - abscess and folliculitis or diffuse - phlegmon or cellulitis, erysipelas, purulent meningitis, phlegmonous cholecistitis/appendicitis)
...............................................................
Fibrinous pericarditis
Fibrinous pericarditis is an exudative inflammation. The visceral pericardium (epicardium) is infiltrated by the fibrinous exudate. This consists in fibrin strands and leukocytes. Fibrin describes an eosinophilic (pink) network, amorphous. Leukocytes (mainly, neutrophils) are found within the fibrin deposits and intrapericardic. Vascular congestion is also present. The myocardium has no changes. (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x4)
Fibrinous pericarditis (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x20)
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Purulent meningitis
Purulent leptomeningitis (suppurative leptomeningitis) is a diffuse purulent inflammation. The leptomeninges (arachnoida and piamater) contain purulent exudate (pus): leukocytes (neutrophils), fibrin, germs, proteins, necrotic debris. Blood vessels in the subarachnoidian space and those intracerebral are congested and neutrophil margination is present. (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x4)
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
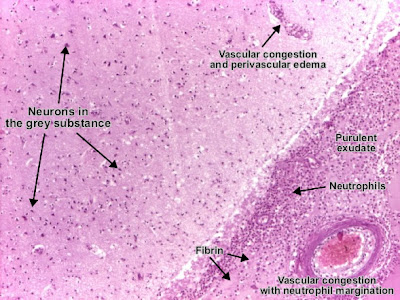
Abscess brain
Abscess is an exudative purulent localized inflammation. In the white matter, a recent abscess consisting in pus : neutrophils (normal or in lisis), fibrin, necrotic debris, germs. Vessels present congestion and important perivascular edema. (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x4)
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Acute pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis is an exudative purulent localized inflammation of kidney and renal pelvis. The renal parenchyma presents in the interstitium abscesses (suppurative necrosis), consisting in purulent exudate (pus): neutrophils, fibrin, cell debris and central germ colonies (hematoxylinophils). Tubules are damaged by exudate and may contain neutrophil casts. In the early stages, glomeruli and vessels are normal. (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x10)
Acute pyelonephritis (Hematoxylin-eosine, ob. x10)
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ

+-+Copy+-+Copy+-+Copy.jpg)