Patholgy Slides : Tumors or Neoplasia
Teratomas and Melanocytic tumors
Teratomas
Benign microcystic teratoma of the ovary (II)
Benign microcystic teratoma of the ovary (III)
Intradermal melanocytic nevus (detail)
اضغط على الصورة للتكبير -ـ Click on image to enlarge size
Teratomas
Benign microcystic teratoma of the ovary
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Teratoma is a tumor which arises from tutipotent germinal cells. Frequently, it is localized in gonads (testis, ovary). It contains a variety of tissues (derived from one, two or three embryonic cell layers - mesoderm, endoderm or ectoderm), tissues which normally are foreign to the site of growth.
Mature teratoma (dermoid cyst) containing well-differentiated structures : respiratory epithelium and nervous tissue - brain. (H&E, ob. x10)
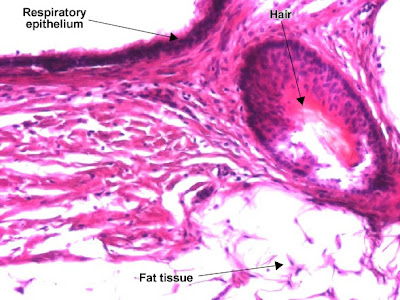
Mature teratoma (dermoid cyst) containing well-differentiated structures : respiratory epithelium, hair follicle and smooth muscle. (H&E, ob. x20)
Mature teratoma (dermoid cyst) containing well-differentiated structures : stratified epithelium, hair and fat tissue. (H&E, ob. x20)
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Melanocytic tumors
Intradermal melanocytic nevus
Nevus cells (melanocytes) are normally localized in the basal layer of the epidermis. Their proliferation may appear in the epidermis (jonctional nevus), in the epidermis and dermis (compound nevus) or only in the dermis (intradermal nevus).
Intradermal melanocytic nevus - a benign tumor in which the tumor cells form nests in the dermis, are regular, round, with central nucleus and single nucleolus. In the supreficial dermis, some melanocytes may produce melanin pigment in the cytoplasm (dark-brown, granular). (H&E, ob.x4)
Intradermal melanocytic nevus (detail). (Hematoxilina-eozina, ob. x10)

+-+Copy+-+Copy+-+Copy.jpg)